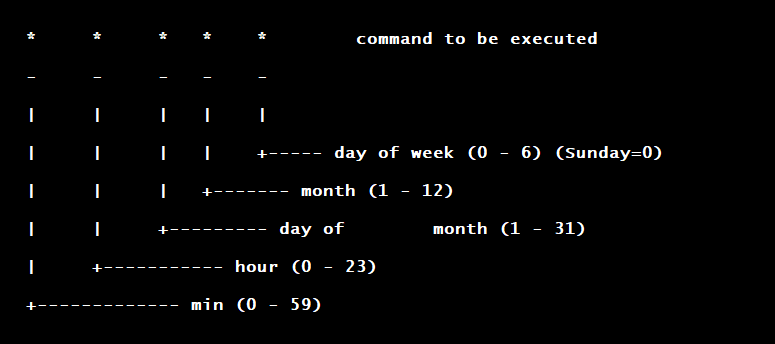Vous désirez planifier des tâches récurentes? Cron est l’outil qu’il vous faut! Voici les details de son utilisation.
Pour éditer les actions du fichier crontab :
sudo crontab -ePour afficher le contenu du fichier crontab :
sudo crontab -lPour supprimer toutes les actions du fichier crontab :
sudo crontab -rEt on redémarre Cron:
sudo service cron reloadVoici de manière schématique la syntaxe à respecter d’un crontab:
# Example of job definition:
# .---------------- minute (0 - 59)
# | .------------- hour (0 - 23)
# | | .---------- day of month (1 - 31)
# | | | .------- month (1 - 12) OR jan,feb,mar,apr ...
# | | | | .---- day of week (0 - 6) (Sunday=0 or 7) OR sun,mon,tue,wed,thu,fri,sat
# | | | | |
# * * * * * user command to be executedmm hh jj MMM JJJ [user] tâche > log- @reboot pour une tâche au redémarrage
- mm : minutes (00-59).
- hh : heures (00-23) .
- jj : jour du mois (01-31).
- MMM : mois (01-12 ou abréviation anglaise sur trois lettres : jan, feb, mar, apr, may, jun, jul, aug, sep, oct, nov, dec).
- JJJ : jour de la semaine (1-7 ou abréviation anglaise sur trois lettres : mon, tue, wed, thu, fri, sat, sun).
- user (facultatif) : nom d’utilisateur avec lequel exécuter la tâche.
- tâche : commande à exécuter.
- > log (facultatif) : redirection de la sortie vers un fichier de log. Si un fichier de log n’est pas spécifié, un mail sera envoyé à l’utilisateur local.
Pour chaque unité, on peut utiliser les notations suivantes :
- 1-5 : les unités de temps de 1 à 5.
- */6 : toutes les 6 unités de temps (toutes les 6 heures par exemple).
- 2,7 : les unités de temps 2 et 7.
Envoi de mail
Par défaut, cron envoie un message à l’utilisateur qui a planifié sa tâche.
Pour ne pas envoyer de façon automatique ce message à l’utilisateur (ou utilisateur@domaine.ext si un agent tel que postfix a été configuré) il faut indiquer sur la première ligne du crontab -e
MAILTO=""